|
|
 |
Home |
About Us |
Learning |
Health |
Course Brochures |
Free Publications |
Products |
Make an Appointment
Internet Consultations |
Forum |
Testimonials |
Shopping |
Discount Vouchers |
Contact Us |
Login |
Register
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nutrition Medicine
|
|
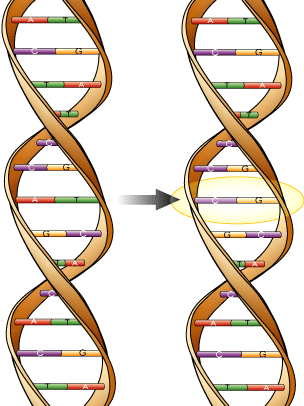
Nutrition Medicine is a new science that is based on the fact that every individual has a different genetic make-up, which leads to different nutritional requirements. When passed on from one generation to the next the genes stay relatively constant, but individual mutations do occur, a phenomenon called Genetic Polymorphisms. In the picture the red-green pair on the left has changed into the purple-yellow pair on the right (yellow ring). Genes code for the proteins in our body. The building blocks of proteins are called amino acids, just as beads are the building blocks of a necklace. The result of these Polymorphisms is that the genes produce a protein that has at least one different amino acid in the chain and this can affect the way the protein folds in space (for more detailed information, please read the free information booklets:
Nutrition and
What is Health?).
|
If the changes are only small, the effect can be hardly noticeable, but on a biochemical scale it may be the difference between a snug fit between a protein and a nutrient or a loose fit. When it is a loose fit, the person may need more of that nutrient to get the same absorption or effect as someone who has a snug fit.
Development Delay, Learning and behaviour difficulties and especially the Autism Spectrum Disorders have a genetic component that renders the child more susceptible to a chemical or environmental insult than other children. Genetic Polymorphisms can account for the fact that one sibling may react poorly to anti-biotics or vaccinations and another sibling does not. In these cases the Polymorphisms have affected an enzyme that is necessary for the detoxification of heavy metals or other toxins, so that the child is not able to remove the toxins ingested with the vaccinations. can When these toxins enter the brain they can (and usually do) interfere with brain function and development.
Nutrition Medicine aims to optimise the:
* intake of nutrients by creating a diet that is best suitable to the individual
* digestion of nutrients
* absorption of nutrients
* gut function
* gut flora
* detoxification pathways in the liver and the cells by giving supplements that
will support these defective pathways
* elimination of toxins and undigested food particles
* production and function of hormones
* production and function of neuro-transmitters
Nutrition Medicine can play an important role in preparing for a healthy pregnancy. To ensure the baby has an optimal chance both parents need to be in optimal nutritional shape. Nutrition Medicine can assist both future parents in optimising their nutritional state before conception to maximise the chances of a healthy pregnancy and healthy Foetal Development. Nutrition Medicine can also assist the future mother during pregnancy and after childbirth to offer both mother and baby the best nutritional advice.
|
|
As we age, the process of digestion and absorption declines. This process of decline already starts at the age of 35. As a result
our brain receives less nutrients and this will affect brain function.
This lack of function can often be overcome by giving extra nutritional
support. |

|
In the last 50 years the prevalence of premature onset of Alzheimer’s disease and other neuro-degenerative diseases is increasing with an alarming rate (see also Health page). Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by brain inflammation. Nutrition Medicine can offer support to counter this inflammation by the use of certain nutrients such as anti-oxidants and phyto-nutrients (nutrients from plants). Blackcurrants, Raspberries (see picture), Blackberries, Blueberries contain Phyto-nutrients that are very beneficial for the ageing brain. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Views: 870648
|

|
|
© Copyright 2008 Optimum Learning & Health Centre, All Rights Reserved. |
|
|
|
|